Second Level Address Translation a.k.a. SLAT is a technology introduced in Intel and AMD processors. Recently released Windows Phone 8 SDK needs it to run the emulator 8 in your Windows 8 system.
So, what is this SLAT and how to check whether your CPU really supports it? In this post, we will discuss this with you.
What is Second Level Address Translation?
SLAT is a Hyper-V Technology introduced in Intel and AMD processors but with a different name. Intel calls it as Extended Page Table (EPT), where as AMD calls it as Rapid Virtualization Indexing (RVI). Intel introduced it in their processors built on Nehalem Architecture and AMD introduced it in their third generation Opteron processors named as Barcelona.
Nahalem micro processors use 45nm process, 4-12 MB L3 cache with integrated memory controller supporting 2/3 memory channels. On the other hand, the Barcelona features a shared L3 cache with 128-bit floating point units in an enhanced micro architecture.
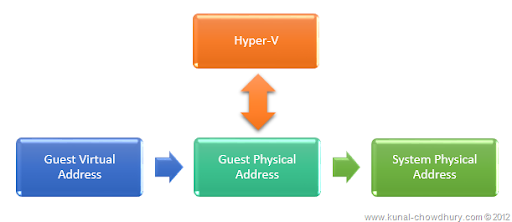
These types of processors have Translation Lookaside Buffer a.k.a. TLB which supports physical memory translation. It is a type of cache that contains all recently uses mappings from the page table on the processor. When it needs virtual address to physical address translation, the TLB unit checks it’s in-built cache to determine the respective mapping information. If it does not contain the respective mapping record, a page error occurs and the OS checks the page table for the mapping information. If the operating system find relative mapping record, it goes to write that in to the TLB (Translation Lookaside Buffer) and the address translation takes place.
This type of Hyper-V (Hyper Visor) technology uses more virtual memory management functions and reduces the overhead of the translation of guest physical address to real physical address. Thus it saves more memory to use it in further processing.
How to check whether your CPU supports SLAT?
If you want to know whether your CPU supports SLAT, you can get that information by following any one of the below two easy steps. First we will use a 3rd party command line utility which will give you the information about your CPU and the 2nd is just a quick trick to get out the information in Windows 8. If you are using Windows 8, I will suggest you to go with the second approach.
First Approach: Using CoreInfo Utility
CoreInfo is a command-line utility that shows you the mapping between logical processors and the physical processor, as well as the cache’s assigned to each logical processor. It uses the Windows’ GetLogicalProcessorInformation function to obtain this information and prints it to the screen, representing a mapping to a logical processor with an asterisk e.g. ‘*’. Coreinfo is useful for gaining insight into the processor and cache topology of your system.
To begin with it, first download the CoreInfo utility from the Microsoft Technet’s Windows Internals Page. Once downloaded, open Windows Command Prompt with Administrator privileges. Now navigate to the downloaded location of the CoreInfo.exe file and enter the following command in your command prompt:
coreinfo.exe - v
This command will dump only virtualization related features including support for second level address translation into your screen which you can verify to see whether your CPU supports that SLAT. This will look similar to this:
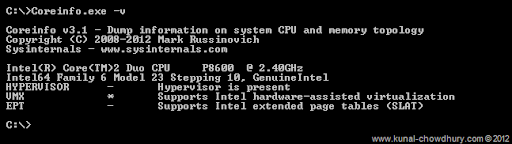
If your CPU supports SLAT, it will have an asterisk ( * ) near to the “EPT” and if it does not support SLAT, you will notice a minus sign ( – ) there. For a complete list of commands and output result details, visit the CoreInfo page here.
Second Approach: Using Simple Windows Tricks
This approach is just a trick to know whether your CPU supports SLAT in Hyper-V mode. To do this, go to “Control Panel – Programs – Turn Windows features on or off” which will open the “Windows Features” window in the screen.
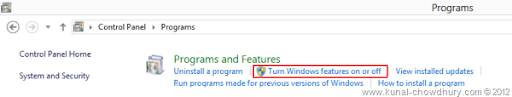
Once the Windows Features screen pops up in the screen, you can see a list of Windows features in that. Among them search for the option that says “Hyper-V” and expand it as below:

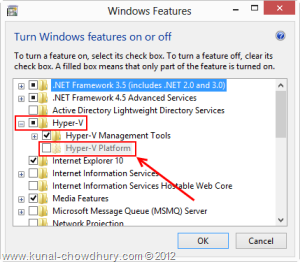
Inside the “Hyper-V” option, you will see a sub key that says “Hyper-V Platform”. If it is enabled, that means that your processor supports “Second Level Address Translation” i.e. SLAT and in case it is disabled, your processor does not support SLAT feature of Hypervision technology.
Further Reading
Here are few references those you may want to study further to know more about Hyper-V, SLAT and Nehalem Intel Micro Processor Architecture:
End Note
I hope that, this post was useful for you to understand the basics about SLAT and the way to find out whether your CPU supports it. If you know any other alternative ways to find this, please drop a line below with the solution and link to help others to find out easily.
Stay tuned with me on Twitter, Facebook and Google+ for updates. Subscribe to my blog’s RSS Feed and email newsletter to get notification directly delivered to your inbox.